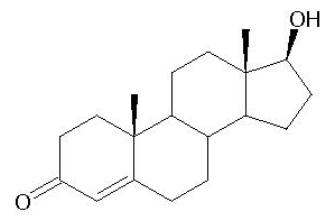
About Testosterone:
Though testosterone is primarily thought of as a male hormone, this steroid hormone is very
important for women's health. Testosterone plays a role in the proper function of sex drive, lean
muscle mass and strength, bone health, mood, cardiac, and blood production. For perimenopausal or menopausal women, testosterone is becoming a common part of hormone replacement therapies. Evaluation of testosterone levels is rapidly becoming a standard part of female hormone evaluation by physicians around the world. In men low testosterone levels been linked to decreased sex drive, impotence, infertility, abnormal breast enlargement, fatigue, depression, lowered motivation, irritability, weight gain, and decreased muscle size and strength. Testosterone levels reach their peak in 20 to 30 year old males, and decline with each passing decade. Low testosterone has also been implicated in decreasing body hair, shrinking of testes and prostate, increased risk for osteoporosis in men, anemia, and thinning of skin with increased wrinkle development. Excess testosterone may be a concern when there is prostate cancer present.
See:
Actions of Testosterone
Production of Testosterone
Pathways:
Androstenedione --> Testosterone --> Estradiol
Androstenediol --> Testosterone --> Estradiol
Common Names: Testosterone; trans-testosterone; delta4- androsten-17b-ol-3-one; 17b-hydroxy-4-androsten-3-one; androlin; Android; Halotensin; Oreton; Testex; Testoderm; Testred; Virilon;17beta-Hydroxyandrost-4-en-3-one; Androst-4-en-3-one, 17-hydroxy-, (17beta)-; 4-androstene-17beta-ol-3-one;
Chemical Name: 17ß-Hydroxyandrost-4-en-3-one
Molecular Formula: C19H28O2
Molecular Weight: 288.429
