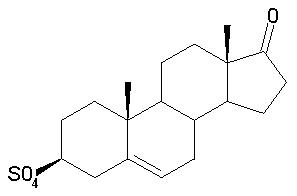
Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulfate (DHEA-S)
DHEA (dehydroepiandrosterone ) is a metabolic hormone intermediate (a building block for hormones) that has some hormonal characteristics of its own. It is an important precursor for estrogens and testosterone. The most accurate way to measure DHEA is to measure it in the stable form that the body keeps it in; DHEA-S (dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate). Even DHEA that is taken by mouth is quickly converted to this more stable form by the body. DHEA-S levels are usually much higher in men than they are in women. Levels peak at about 25-30 years of age and decline with aging. The decline of DHEA levels with aging correlates with a general decline in immunity, and lowering resistance to age-related diseases. Decreased DHEA levels are noted in many chronic illnesses, obesity, decreased sex drive (low libido), chronic fatigue, rheumatological disorders, insomnia, and depression.
DHEA-S is one of the most important hormones produced by the adrenal glands, and should be evaluated in with cortisol another very important adrenal gland. It should also be looked at whenever testosterone levels are low, since it is a precursor to testosterone.
Pathway: Dehydroepiandrosterone «
Dehydroepiandrosterone-Sulfate
Common Names: Dehydroepiandrosterone-Sulfate; DHEA- Sulfate
Chemical Name: 3beta-Hydroxyandrost-5-en-17-one 3-sulfate
Molecular Formula: C19H28O5S
Molecular Weight: 368.4872
